LOOK
Look disk scheduling is another type of disk scheduling algorithm. Look scheduling is an enhanced version of SCAN disk scheduling. Look disk scheduling is the same as SCAN disk scheduling, but in this scheduling, instead of going till the last track, we go till the last request and then change the direction.
Advantages:
- In Look disk scheduling, there is no starvation.
- Look disk scheduling offers low variance in waiting time and response time.
- Look disk scheduling offers better performance as compared to the SCAN disk scheduling.
- In look disk scheduling, there is no requirement of disk head to move till the end to the disk when we do not have any request to be serviced.
Disadvantages:
- There is an overhead of finding the end requests.
- It causes long waiting time for the cylinders just visited by the head.
Example:
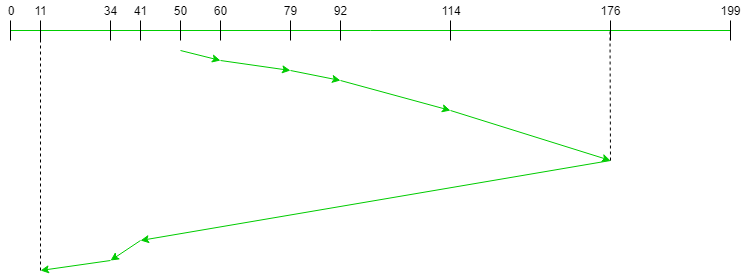
- Consider a disk containing 200 tracks (0-199) and the request queue includes the track number 176, 79, 34, 60, 92, 11, 41, 114 respectively. The current position of read//write head is 50, and direction is towards the larger value.
- Calculate the total number of cylinders moved by the head using the LOOK algorithm.
- The disk contains 200 tracks varied from 0 - 199. The current position of R/W head is at 50. So calculate total number of cylinder moved by head.
-
Total Number of cylinders moved by head
= (60-50)+(79-60)+(92-79)+(114-92)+(176-114)+(176-41)+(41-34)+(34-11)
= 291
Steps to Implement Algorithm:
- Let Request array represents an array storing indexes of tracks that have been requested in ascending order of their time of arrival. 'head' is the position of disk head.
- The initial direction in which head is moving is given and it services in the same direction.
- The head services all the requests one by one in the direction head is moving.
- The head continues to move in the same direction until all the request in this direction are finished.
- While moving in this direction calculate the absolute distance of the track from the head.
- Increment the total seek count with this distance.
- Currently serviced track position now becomes the new head position.
Time Complexity: O ( N * logN ) Auxiliary Space: O ( N )
Simulate